Ultimate Guide to Bathroom Design with Focus on Anti Slip and Safety Features
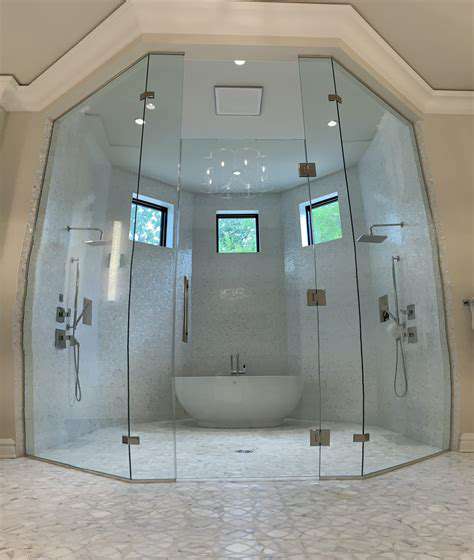

Understanding the Importance of Safety
Designing a safe environment isn't just about compliance—it's about creating peace of mind. When safety becomes an integral part of the design process, it transforms spaces into havens where users feel protected and comfortable. This philosophy applies particularly to bathrooms, where wet surfaces and hard materials present unique challenges.
Identifying Potential Hazards
The first rule of bathroom safety? Assume nothing. Every element requires scrutiny—from the height of shower thresholds to the texture of flooring materials. Water temperature controls, electrical outlet placements, and even the weight of bathroom doors all represent potential risks that demand careful evaluation. It's this meticulous attention to detail that separates adequate designs from exceptional ones.
Implementing Protective Measures
Modern bathrooms incorporate innovative safety features that blend seamlessly with aesthetics. Temperature-regulated faucets prevent scalding, while motion-activated lighting eliminates fumbling for switches with wet hands. These solutions demonstrate how thoughtful design can address safety concerns without compromising style or functionality.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
While building codes provide essential safety baselines, truly exceptional designs exceed these minimum requirements. For instance, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) specifies grab bar dimensions, but premium installations consider additional factors like bar texture and visual contrast against surrounding walls for users with limited vision.
Training and Communication Protocols
Safety extends beyond physical installations. Clear instructional signage about proper shower seat usage or emergency contact information placement can make critical differences during accidents. Many luxury hotels now include bathroom safety briefings in their guest orientation—a practice residential designers might consider adapting through customized homeowner manuals.
Evaluating and Maintaining Safety Measures
The most comprehensive safety plan remains ineffective without proper upkeep. Establishing a quarterly bathroom safety checklist—testing grab bar stability, inspecting non-slip surfaces, verifying drain function—creates a systematic approach to hazard prevention. This proactive maintenance routine ensures long-term protection as materials age and household needs evolve.
Elevating the Safety of Shower and Tub Areas
Improving Shower and Tub Drainage
Drainage systems represent the unsung heroes of bathroom safety. Contemporary designs now incorporate linear drains that eliminate tripping hazards while providing faster water evacuation. Some premium models feature built-in hair catchers that simplify maintenance—a small detail that prevents major plumbing issues.
Utilizing Slip-Resistant Surfaces
The science of slip resistance has evolved dramatically. Today's textured surfaces use microscopic patterns that increase traction without feeling rough underfoot. Porcelain tiles now achieve 0.6+ COF (coefficient of friction) ratings—comparable to rough concrete—while maintaining elegant appearances. These advancements prove safety and sophistication aren't mutually exclusive.
Implementing Proper Lighting
Strategic lighting addresses multiple safety concerns simultaneously. LED strips along shower bases improve visibility while serving as night lights. Color-changing options can indicate water temperature—blue for cold, red for hot—creating intuitive safety cues. Such innovations demonstrate how lighting serves functional purposes beyond basic illumination.
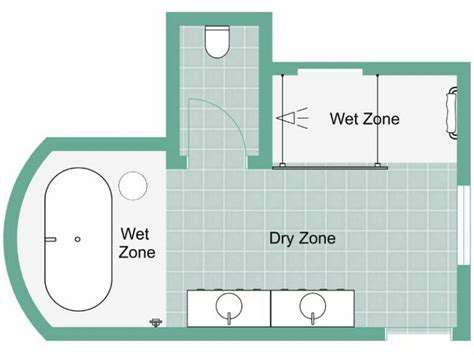
Ensuring Proper Barrier-Free Design
The barrier-free movement has redefined accessible design. Curbless showers with slight (1-2%) slopes prevent water runoff while maintaining seamless transitions. Floating vanities create clear floor space for mobility devices. These features benefit everyone—from parents bathing children to athletes recovering from injuries—proving universal design principles create better spaces for all users.
Selecting Durable and Water-Resistant Materials
Material science breakthroughs have introduced options like quartz surfacing that resist stains, scratches, and bacteria growth. New antimicrobial grouts inhibit mold formation—a significant advancement for respiratory health. These materials demonstrate how product innovation contributes to long-term bathroom safety and hygiene.
Maintaining Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Smart home technology now assists with bathroom maintenance. Leak detectors alert homeowners to pipe issues before water damage occurs. Digital shower systems track usage patterns that might indicate mobility changes requiring safety modifications. This integration of technology and preventative care represents the future of bathroom safety management.
Precision in design yields measurable safety improvements. Research shows properly placed grab bars reduce fall injuries by 80% among seniors. Thermostatic mixing valves that maintain water temperature within 2°F variations prevent an estimated 3,800 emergency room visits annually from scalding accidents.

Illuminating Your Bathroom for Enhanced Visibility
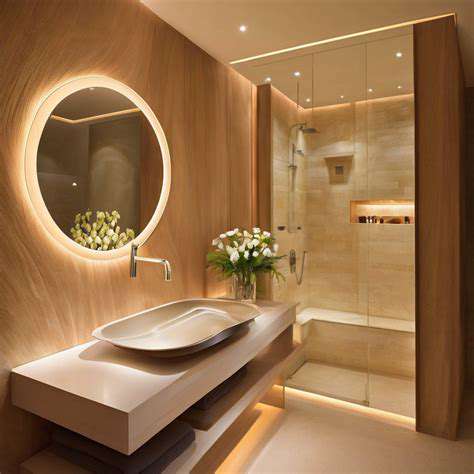

Lighting Strategies for a Modern Bathroom
Effective lighting design follows the three-layer principle: ambient (general), task (specific), and accent (decorative) lighting. This approach creates visual hierarchy while ensuring all functional needs receive proper illumination. In bathrooms, this might combine recessed ceiling lights (ambient), mirror-side vertical strips (task), and niche spotlights (accent).
Ambient Lighting: Setting the Mood
Contemporary ambient solutions include luminous ceilings that diffuse light evenly, reducing harsh shadows. Color-tunable systems that adjust from energizing cool white (5000K) in mornings to relaxing warm white (2700K) at night support circadian rhythms. Such systems demonstrate how lighting can address both visibility and wellness concerns.
Task Lighting: Illuminating Specific Areas
The vanity area demands particular attention. Vertical lighting positioned at 60-66 inches from the floor on both sides of mirrors eliminates facial shadows that distort makeup application or shaving. Newer LED technologies provide 90+ CRI (Color Rendering Index) for true-color representation—critical for personal grooming accuracy.
Accent Lighting: Adding Visual Interest
Innovative accent lighting now serves dual purposes. LED strips beneath floating vanities provide both aesthetic appeal and nighttime path lighting. Backlit mirrors create focal points while improving facial visibility. These examples show how accent features can simultaneously enhance safety and design.
Natural Light Integration: Maximizing Daylight
Privacy glass technologies now allow abundant natural light without compromising seclusion. Switchable glass that transitions from clear to opaque with the flip of a switch represents one solution. Another approach uses strategically placed clerestory windows that admit light while maintaining privacy. Such innovations reconcile the competing demands of illumination and personal space.
Energy-Efficient Lighting Options: Saving Money and the Planet
The latest LED advancements include fixtures with integrated occupancy sensors and automatic dimming capabilities. Some systems connect to home networks, allowing voice control and scheduling. These smart solutions can reduce bathroom lighting energy use by up to 80% compared to traditional incandescent systems. The combination of sustainability and convenience makes them increasingly popular choices.
Read more about Ultimate Guide to Bathroom Design with Focus on Anti Slip and Safety Features
Hot Recommendations
- Trendy Kitchen Interiors: Open Concepts and Smart Storage Solutions
- Expert Multi Functional Room Ideas for Combining Entertainment with Fitness
- Modern Home Office Inspirations for a Study That Merges Work and Leisure
- Modern Bathroom Design Ideas for Optimizing Small Spaces and Safety
- Expert Strategies for a Children's Room That Inspires Growth and Imagination
- Modern Bathroom Inspirations for a Space That Prioritizes Safety and Efficiency
- Creative Multi Functional Space Ideas for a Room That Combines Gym and Media
- Modern Techniques for a Multi Purpose Room That Enhances Home Entertainment and Fitness
- Expert Guide to Balancing Modern Art and Functional Living Room Layouts
- Expert Tips for a Children's Room That Balances Play, Learning, and Security